Steel manufacturing sites
Illustrates the process from raw materials (e.g., iron ore) to finished steel products. Describes specific detectors designed to address hazards posed by the byproduct gases generated during each process.
Illustrates the process from raw materials (e.g., iron ore) to finished steel products. Describes specific detectors designed to address hazards posed by the byproduct gases generated during each process.
Overview of individual processes from raw material input to steel manufacture
Steel manufacturing processes generate combustible and toxic gas mixtures known as B gas, C gas, and LD gas.
Since the mixed gas generated during the manufacturing process contains high concentrations of CO, H2, and CH4, it is necessary to be careful about leakage in terms of both toxic and combustible gas.
Iron ore and coal (coke), the major raw materials for iron, are transported by cargo ship.
The raw materials are treated before the pig iron manufacturing process to form sintered ore and coke.
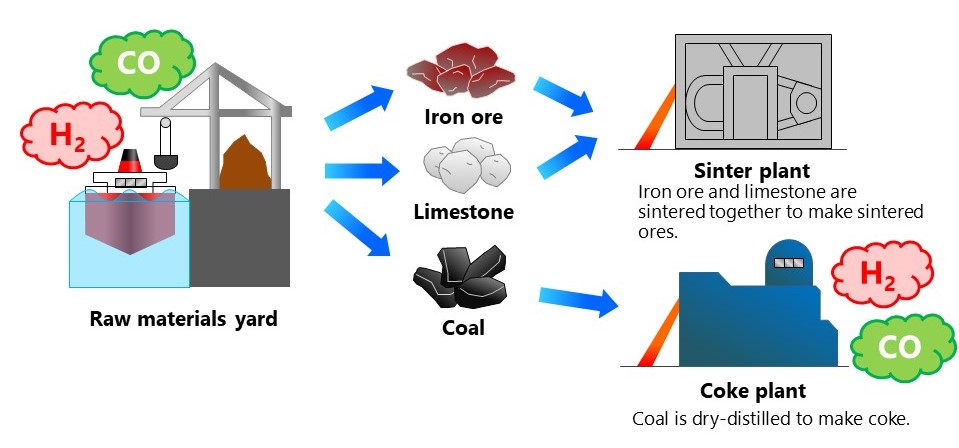
There is a risk of oxygen deficient atmospheres in enclosed spaces due to oxygen depletion caused by the oxidation of coal and iron ore, and examples of such spaces include ship holds. Precautions are also required to prevent even small leaks, as the COG produced in coking plants is both a combustible and toxic gas mixture.
Fixed combustible gas detectors

Model: SD-3
Flame detectors

Model: GD-A80
For wearing by workers

Model: 04 Series
The byproduct gas produced inside steel manufacturing plants is mixed and used as a fuel to generate electricity.
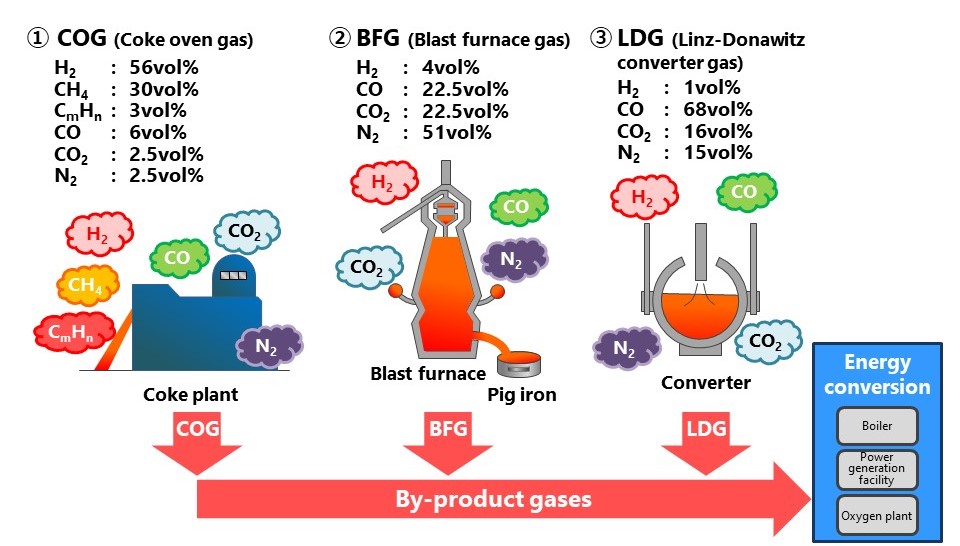
The constituents of the byproduct gas mixture must be confirmed, as the types and ratios of which in the mixture differ depending on the specific plant and operating conditions.
Ingredient confirmation

Model: OHC-800
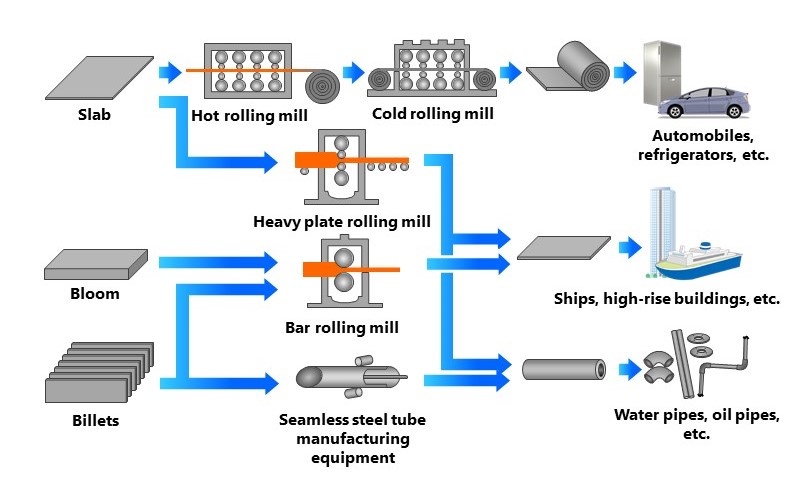
The individual steel plates cut at the continuous casting facility undergo a range of processes to achieve the desired shapes.
Fixed gas detectors are recommended for the following applications:
Portable gas detectors are recommended for the following applications: